O先生はCygwinでGithubとの連携を公開鍵・秘密鍵、作成の流れを教えてくれたんですが、Gitでの接続もしちゃってるし、いずれにせよVSCodeでのプッシュが便利なので以下を参考にしますw
https://zenn.dev/ojk/books/github-vscode/viewer/vscode-git
ipyn
ジュピターでやった方が使いやすいので拡張子を変えてみます
それで最近ジュピターとVSコードの連携のセキュリティが厳しくなったとのことでパスワードの設定がカーネルで求められたので
AnacondaのCMDで設定しました。つら・・・
Microsoft Windows [Version 10.0.22631.4169]
(c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
(base) C:\Users\sae202311>python
Python 3.10.9 | packaged by Anaconda, Inc. | (main, Mar 1 2023, 18:18:15) [MSC v.1916 64 bit (AMD64)] on win32
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>> from notebook.auth import passwd
>>> passwd()
Enter password:
Verify password:
Passwords do not match.
Enter password:
Verify password:
'argon2:$argon2id$v=19$m=10240,t=10,p=8$17fy/fkQh+o/FB3BPq894A$aHg/QO75Ab4Iv4TlSLQ0h3rjF+e1F5/+MShydbGYz58'
>>>こちらが出てきました。
ので、Textfileにて編集。
テキストのURLは”C:\Users\sae202311\venv\Lib\site-packages\flask\config.py”になりますなんか今見ると全然違うところにやってるな。。。。なので間違いなのですが、一応こんな感じで最後の一行に追記したのが以下になります。
このコードの文末見ればわかると思いますが間違いですwwww
from __future__ import annotations
import errno
import json
import os
import types
import typing as t
from werkzeug.utils import import_string
if t.TYPE_CHECKING:
import typing_extensions as te
from .sansio.app import App
T = t.TypeVar("T")
class ConfigAttribute(t.Generic[T]):
"""Makes an attribute forward to the config"""
def __init__(
self, name: str, get_converter: t.Callable[[t.Any], T] | None = None
) -> None:
self.__name__ = name
self.get_converter = get_converter
@t.overload
def __get__(self, obj: None, owner: None) -> te.Self: ...
@t.overload
def __get__(self, obj: App, owner: type[App]) -> T: ...
def __get__(self, obj: App | None, owner: type[App] | None = None) -> T | te.Self:
if obj is None:
return self
rv = obj.config[self.__name__]
if self.get_converter is not None:
rv = self.get_converter(rv)
return rv # type: ignore[no-any-return]
def __set__(self, obj: App, value: t.Any) -> None:
obj.config[self.__name__] = value
class Config(dict): # type: ignore[type-arg]
"""Works exactly like a dict but provides ways to fill it from files
or special dictionaries. There are two common patterns to populate the
config.
Either you can fill the config from a config file::
app.config.from_pyfile('yourconfig.cfg')
Or alternatively you can define the configuration options in the
module that calls :meth:`from_object` or provide an import path to
a module that should be loaded. It is also possible to tell it to
use the same module and with that provide the configuration values
just before the call::
DEBUG = True
SECRET_KEY = 'development key'
app.config.from_object(__name__)
In both cases (loading from any Python file or loading from modules),
only uppercase keys are added to the config. This makes it possible to use
lowercase values in the config file for temporary values that are not added
to the config or to define the config keys in the same file that implements
the application.
Probably the most interesting way to load configurations is from an
environment variable pointing to a file::
app.config.from_envvar('YOURAPPLICATION_SETTINGS')
In this case before launching the application you have to set this
environment variable to the file you want to use. On Linux and OS X
use the export statement::
export YOURAPPLICATION_SETTINGS='/path/to/config/file'
On windows use `set` instead.
:param root_path: path to which files are read relative from. When the
config object is created by the application, this is
the application's :attr:`~flask.Flask.root_path`.
:param defaults: an optional dictionary of default values
"""
def __init__(
self,
root_path: str | os.PathLike[str],
defaults: dict[str, t.Any] | None = None,
) -> None:
super().__init__(defaults or {})
self.root_path = root_path
def from_envvar(self, variable_name: str, silent: bool = False) -> bool:
"""Loads a configuration from an environment variable pointing to
a configuration file. This is basically just a shortcut with nicer
error messages for this line of code::
app.config.from_pyfile(os.environ['YOURAPPLICATION_SETTINGS'])
:param variable_name: name of the environment variable
:param silent: set to ``True`` if you want silent failure for missing
files.
:return: ``True`` if the file was loaded successfully.
"""
rv = os.environ.get(variable_name)
if not rv:
if silent:
return False
raise RuntimeError(
f"The environment variable {variable_name!r} is not set"
" and as such configuration could not be loaded. Set"
" this variable and make it point to a configuration"
" file"
)
return self.from_pyfile(rv, silent=silent)
def from_prefixed_env(
self, prefix: str = "FLASK", *, loads: t.Callable[[str], t.Any] = json.loads
) -> bool:
"""Load any environment variables that start with ``FLASK_``,
dropping the prefix from the env key for the config key. Values
are passed through a loading function to attempt to convert them
to more specific types than strings.
Keys are loaded in :func:`sorted` order.
The default loading function attempts to parse values as any
valid JSON type, including dicts and lists.
Specific items in nested dicts can be set by separating the
keys with double underscores (``__``). If an intermediate key
doesn't exist, it will be initialized to an empty dict.
:param prefix: Load env vars that start with this prefix,
separated with an underscore (``_``).
:param loads: Pass each string value to this function and use
the returned value as the config value. If any error is
raised it is ignored and the value remains a string. The
default is :func:`json.loads`.
.. versionadded:: 2.1
"""
prefix = f"{prefix}_"
len_prefix = len(prefix)
for key in sorted(os.environ):
if not key.startswith(prefix):
continue
value = os.environ[key]
try:
value = loads(value)
except Exception:
# Keep the value as a string if loading failed.
pass
# Change to key.removeprefix(prefix) on Python >= 3.9.
key = key[len_prefix:]
if "__" not in key:
# A non-nested key, set directly.
self[key] = value
continue
# Traverse nested dictionaries with keys separated by "__".
current = self
*parts, tail = key.split("__")
for part in parts:
# If an intermediate dict does not exist, create it.
if part not in current:
current[part] = {}
current = current[part]
current[tail] = value
return True
def from_pyfile(
self, filename: str | os.PathLike[str], silent: bool = False
) -> bool:
"""Updates the values in the config from a Python file. This function
behaves as if the file was imported as module with the
:meth:`from_object` function.
:param filename: the filename of the config. This can either be an
absolute filename or a filename relative to the
root path.
:param silent: set to ``True`` if you want silent failure for missing
files.
:return: ``True`` if the file was loaded successfully.
.. versionadded:: 0.7
`silent` parameter.
"""
filename = os.path.join(self.root_path, filename)
d = types.ModuleType("config")
d.__file__ = filename
try:
with open(filename, mode="rb") as config_file:
exec(compile(config_file.read(), filename, "exec"), d.__dict__)
except OSError as e:
if silent and e.errno in (errno.ENOENT, errno.EISDIR, errno.ENOTDIR):
return False
e.strerror = f"Unable to load configuration file ({e.strerror})"
raise
self.from_object(d)
return True
def from_object(self, obj: object | str) -> None:
"""Updates the values from the given object. An object can be of one
of the following two types:
- a string: in this case the object with that name will be imported
- an actual object reference: that object is used directly
Objects are usually either modules or classes. :meth:`from_object`
loads only the uppercase attributes of the module/class. A ``dict``
object will not work with :meth:`from_object` because the keys of a
``dict`` are not attributes of the ``dict`` class.
Example of module-based configuration::
app.config.from_object('yourapplication.default_config')
from yourapplication import default_config
app.config.from_object(default_config)
Nothing is done to the object before loading. If the object is a
class and has ``@property`` attributes, it needs to be
instantiated before being passed to this method.
You should not use this function to load the actual configuration but
rather configuration defaults. The actual config should be loaded
with :meth:`from_pyfile` and ideally from a location not within the
package because the package might be installed system wide.
See :ref:`config-dev-prod` for an example of class-based configuration
using :meth:`from_object`.
:param obj: an import name or object
"""
if isinstance(obj, str):
obj = import_string(obj)
for key in dir(obj):
if key.isupper():
self[key] = getattr(obj, key)
def from_file(
self,
filename: str | os.PathLike[str],
load: t.Callable[[t.IO[t.Any]], t.Mapping[str, t.Any]],
silent: bool = False,
text: bool = True,
) -> bool:
"""Update the values in the config from a file that is loaded
using the ``load`` parameter. The loaded data is passed to the
:meth:`from_mapping` method.
.. code-block:: python
import json
app.config.from_file("config.json", load=json.load)
import tomllib
app.config.from_file("config.toml", load=tomllib.load, text=False)
:param filename: The path to the data file. This can be an
absolute path or relative to the config root path.
:param load: A callable that takes a file handle and returns a
mapping of loaded data from the file.
:type load: ``Callable[[Reader], Mapping]`` where ``Reader``
implements a ``read`` method.
:param silent: Ignore the file if it doesn't exist.
:param text: Open the file in text or binary mode.
:return: ``True`` if the file was loaded successfully.
.. versionchanged:: 2.3
The ``text`` parameter was added.
.. versionadded:: 2.0
"""
filename = os.path.join(self.root_path, filename)
try:
with open(filename, "r" if text else "rb") as f:
obj = load(f)
except OSError as e:
if silent and e.errno in (errno.ENOENT, errno.EISDIR):
return False
e.strerror = f"Unable to load configuration file ({e.strerror})"
raise
return self.from_mapping(obj)
def from_mapping(
self, mapping: t.Mapping[str, t.Any] | None = None, **kwargs: t.Any
) -> bool:
"""Updates the config like :meth:`update` ignoring items with
non-upper keys.
:return: Always returns ``True``.
.. versionadded:: 0.11
"""
mappings: dict[str, t.Any] = {}
if mapping is not None:
mappings.update(mapping)
mappings.update(kwargs)
for key, value in mappings.items():
if key.isupper():
self[key] = value
return True
def get_namespace(
self, namespace: str, lowercase: bool = True, trim_namespace: bool = True
) -> dict[str, t.Any]:
"""Returns a dictionary containing a subset of configuration options
that match the specified namespace/prefix. Example usage::
app.config['IMAGE_STORE_TYPE'] = 'fs'
app.config['IMAGE_STORE_PATH'] = '/var/app/images'
app.config['IMAGE_STORE_BASE_URL'] = 'http://img.website.com'
image_store_config = app.config.get_namespace('IMAGE_STORE_')
The resulting dictionary `image_store_config` would look like::
{
'type': 'fs',
'path': '/var/app/images',
'base_url': 'http://img.website.com'
}
This is often useful when configuration options map directly to
keyword arguments in functions or class constructors.
:param namespace: a configuration namespace
:param lowercase: a flag indicating if the keys of the resulting
dictionary should be lowercase
:param trim_namespace: a flag indicating if the keys of the resulting
dictionary should not include the namespace
.. versionadded:: 0.11
"""
rv = {}
for k, v in self.items():
if not k.startswith(namespace):
continue
if trim_namespace:
key = k[len(namespace) :]
else:
key = k
if lowercase:
key = key.lower()
rv[key] = v
return rv
def __repr__(self) -> str:
return f"<{type(self).__name__} {dict.__repr__(self)}>"
c.NotebookApp.password = 'argon2:$argon2id$v=19$m=10240,t=10,p=8$17fy/fkQh+o/FB3BPq894A$aHg/QO75Ab4Iv4TlSLQ0h3rjF+e1F5/+MShydbGYz58'
↑これですね。削除して保存しておきます。
相当無駄な時間を過ごしました・・・
で、AnacondaのCMDで現在のPythonのバージョンを確認。
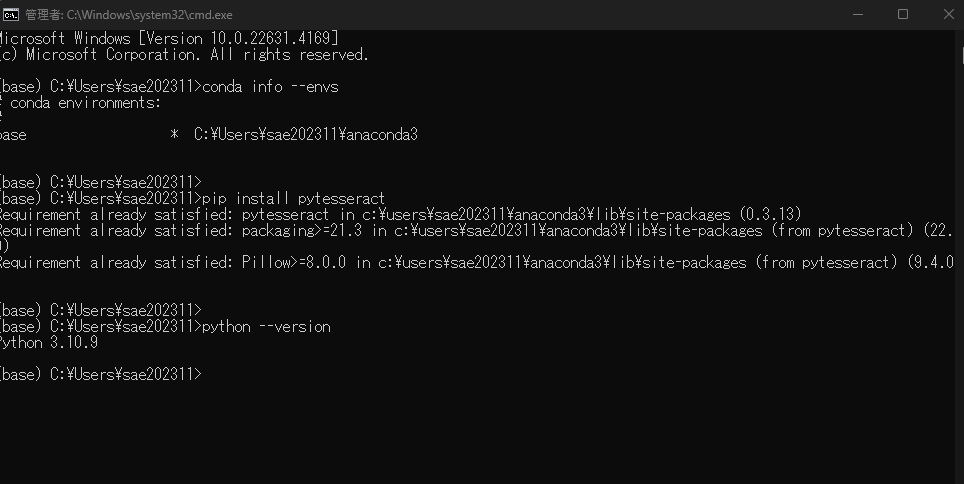
カーネルのバージョンが違うことを確認!あ~すっきりした。
こちらを合わせてから実行して問題なしになりました
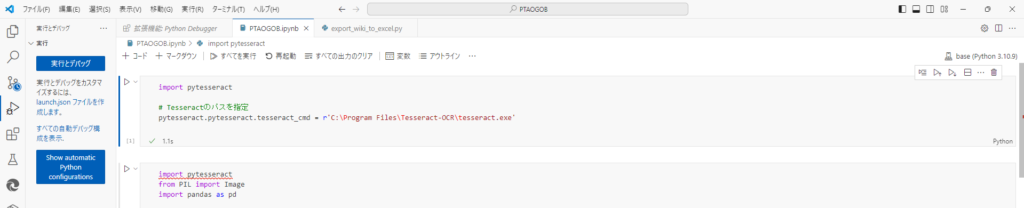
連携完了!すっきし
Share this content: